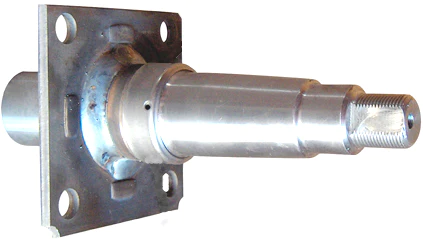
Product Description
45mm Square Straight Stub Axle in slimline profile is commonly used on larger wide trailers and caravans.Stub axle is rated to 775kg per stub or 1450kg for a pair of stub axles.
Bearing Sizes are
- Inner ID 35.00mm, OD 59.10mm
- Outer ID 22.00mm, OD 45.20mm
- Seal ID 43.9mm, OD 59.10mm
- Grease Cap 45.20mm
Products Description:
- Capacity(T):2
- Track(mm):375
- Beam(mm):45×45
- Brake Size(mm):No
- Stubs:5xM16
- PCDxCBD(mm):140×94
- Bearing:35715-35719
- Weight(Kg):13
| Part Number | Wheel Load | Axle Load | PCD | Center Bore Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA012 | 1000 kgs | 2000KG | 5-140 | 94MM |
BUILDING A STRAIGHT BEAM AXLE – SHIM METHOD
NOTE – Building your own axles should only be undertaken by a skilled and proficient welder. Good weld penetration with no porosity or undercut is required to ensure the strength and integrity of the axle is not compromised. If you have any doubts about your skills, leave axle building to the professionals, poorly built and poorly welded axles can cause accidents and kill people.
Straight Beam Axle Setup – Shim Method
There are many ways of setting up stub axles within axle tubes correctly, the following is a tried and tested method that almost anyone with minimal equipment can accomplish.
Getting the stub axles perfectly parallel and true to each other is the difficult part of building your own axle. Getting it wrong will cause a multitude of problems, from poor trailer tracking behind the tow vehicle, premature bearing failure, excessive tyre wear, blowouts and even broken stub axles.
If like most home workshops, you will be lacking a lathe with a 4 jaw chuck and head bore to handle a 50 x 50 piece of axle tube or have a bed length to cope with a full length trailer axle, so you will have to improvise to compensate.
If you are not using machined line pipe for your axle tubes, you will need the following equipment –
• Vernier calipers with internal jaws
• A new tape measure (no wear/sloppiness and easier to read)
• Selection of shim steel including some various sizes of panel steel 0.5 to 1.0mm thick
• Tin snips/shears and scissors (don’t use your wifes ones!)
• Soft face hammer (a shot filled hammer is ideal)
• Set of flat files
• Square
• Flat straight work surface
Ideally you want to get a cheap set of bearings to match the good ones in you new hubs. Using a brass or mild steel drift, carefully remove the good bearing cups from the hubs (put them away somewhere nice and clean) and fit the cheapies. You will need the hubs to be dry fitted (no grease) to the stub axles later on to double check measurements and it is preferable not to do any welding or dusty work in and around your good bearings.
A note about welding axles – to prevent damage to the hub, bearings and stub axle, earthing the axle must be done through the axle tube only. If necessary, tack weld a tab or bolt to the axle tube to allow easy attachment of the earth clamp.
An issue with using ERW/welded pipe as axle tubing is the seam weld internally running the length of the pipe. You can work around this if the seam is of a consistent depth or offset from the centreline of the section (SHS only), but the best thing is to get rid of it. If you are able to access one, beg, borrow or buy an electric file (like a belt sander in miniature). This will considerably reduce the time, frustration and damaged fingers from doing the job manually.
The second best option is to tack weld a 250mm long, 2nd cut or bastard file CHINAMFG the end of a length of 25 x 25 hollow section or similar. This will give the file extra leverage and cutting power and assists in getting deep inside the axle tube.
Clamp the axle tube to whatever will hold it steady and with the seam at the bottom, pass the modified file over the seam and file it flat. You will only need to file around 150-200mm of the seam at each end of the axle tube, but take care that you do not file past the seam especially at the outer edge of the tube. Here there is a tendency to taper off at the opening.
Axle tube length for straight beam axles is pretty straight forward, if the stub axle has a hydraulic caliper yoke or drum brake backing plate mount, the axle tube can butt up against the flat surface of these and welded around. This doesn’t work in all situations, and you may need to set the axle tube 20 mm or more back from the yoke/plate to get good stub axle alignment and weld penetration.
If a non braking stub axle is being fitted, the axle tube should not be closer than 25mm from the seal shoulder (the last bit of machined surface).
With the hub dry fitted (with the cheap bearings), measure from the hub face back to the 25mm mark on the stub axle. Double this measurement and subtract it from the original hub to hub face measurement. This is the axle tube length.
Once the axle tube has been cut to length, remove any burrs inside and outside and if required, file the internal seam flat.
Drill a couple of plug holes in the axle tube at least 12mm diameter, preferably larger so that the stub axle can be secured at the back end with some good welds.
With the Vernier calipers, measure across the inside flats of the axle tube and the diameter of the stub axle. Find the difference between the 2 (the total gap) and divide by 2.
Cut up 4 sets of shims, for each stub axle, to the thickness of the ½ gap measurement. If using a mix of thick and thin shims, try to slip the thin sections inside a sandwich of thicker shims and use a thin layer of grease/oil to help keep the shims together. The shims should ideally be as long as the internal section of stub axle.
Slide the shims and stub axle into the axle tube to assist the stub axle to centralise. With round axle tube, set the shims at either quarters or thirds around the stub axle. On the square axle tube, centre the shims on the flats where the stub axle will contact.
The shims and stub axle should slide nicely into the axle tube and may require a couple of shim adjustments to get right.
Once the stub axle is at the correct position in the axle tube, do a couple of checks to ensure that the hub face to hub face measurement is correct and that the axle tube is central to the hubs.
Tack weld the stub axles in position and start taking 3 or 4 point measurements from hub face to hub face around the hubs. This measurement is critical to getting the hubs exactly parallel to each other. If adjustment is needed, use the soft face hammer to tap the hubs until all measurements are exact.
Lay another tack weld on each stub axle, check your 3 or 4 point measurement and repeat until the stub axle has at least 3 or 4 good tack welds.
Tack weld through the plug weld holes to secure the back end of the stub axle.
Set your welder so that you can lay a good hot penetrating weld (practice on some scrap steel) and fully weld around the stub axle and axle tube. Don’t worry too much about the shims, if you wish to remove them before welding do so, but you can leave them to become part of the axle.
Fill the plug weld holes up until the weld is flush with the top of the axle tube.
Let the axle cool down slowly – do not quench or spray with water! Doing so can cause hardening of the steel around the weld and creating a weak, fatigue prone, stress area.
Once cool, double check the mark at the centre of the axle tube. Remark if necessary and use this to mark out and drill your spring centre holes. Spring centre holes need to be around 15mm diameter. As always, double check your measurements before drilling. In some cases, you may find yourself drilling into the back end of the stub axle. Drill deep enough so that there is clearance for the spring bolt head to fit.
If fitting spring retaining plates, now is the time to weld these on. Welds on spring retaining plates should only be done axially with the axle tube and not across the face of the axle.
Tidy up any slag or welding spatter and file or grind any sharp edges.
Remove the hubs, knock out the cheap bearing cups, give the hubs a good clean and pack and fit the good bearings and seals to your new axles.
If you are painting the axle, use a good zinc rich etch primer coat and a couple of 2 pot enamel top coats to finish off.
If you are plHangZhou on galvanising your axle, drill a 10mm drain hole both ends of the axle tube, at the position where the back end of the stub axle sits. If your spring centre holes line up with the end of the stub axle, this would be a bonus.
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery Co., Ltd is a professional manufacturer of trailer parts in HangZhou, ZHangZhoug Province, China since 2016.
We can produce many trailer parts & accessories as follows: Towbars, axles, brake drums, hubs, brake disc, bearings, springs and springs and suspension kits, couplings, mudguards, U-Bolts, Jockey Wheels, keel rollers and brackets, wobble roller, wheel spacer, equalizers and all accessories related to trailers.
If you can send me the drawings or specifications of the trailer parts, mechanical parts and wheels, we can give you our price.
Q1: Do you have factory?
A: Yes, we have our own factory, own engineers, we can meet custom’s unique requirement.
Q2: Can I have a sample order?
A: Yes, welcome sample order to test and check quality. Mixed samples are acceptable.
Q3: It’s OK to print my logo on your product?
A: Yes, we can according to your exact requirement.
Q4:How do you ship the goods and how long does it take arrive?
A: We usually shipped by DHL, UPS, FedEx, it usually takes 3-5 days to arrive. Airline and sea shipping also optional.
Q5: What is your advantages?
A: We are professional supplier for more than 10 years, we always put the quality and price at the first place. At the same time, our products are exported to various countries, we have full experience to solve thorny problems.
If you want to know about our products and us, welcome to enquiry and email me.thanks
1-Welcome OEM
- You can use your own brands or ours, if you use our brand, our professional team will help you design the packing.
2-Our service
- You inquiry related to our products or prices will be replied in 24 hours.
- Well-trained and experienced staffs to answer all your enquirys in fluent English.
- Protection of your sales area, ideas of your design and all your private information.
- We have a QC team, every product will be checked by them before packed.
3-Welcome to visit
- When you come to our company visit us, we will arrange a car for picking up and help you book hotel. If you want to visit the local scenic spot, our colleague will accompany you.
4-Warranty
- Customer should be provide the video and the pictures for the problem products.
- Products returned within the warranty period must bear product number & date code.
5-After service
- In production and after delivery, we will track on time and tell you goods situation.
- When the goods arrived, if you find any design and quality questions, or difference from your samples, please feel free to contact us, we will find the question and solve it with you.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Axle Number: | 2 |
| Application: | Trailer |
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What safety considerations should be taken into account when using trailer spindles in towing?
When using trailer spindles in towing, several safety considerations should be taken into account. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Proper Installation: Ensure that the trailer spindles are installed correctly according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. This includes securely attaching the spindles to the trailer frame and using appropriate hardware and torque specifications. Improper installation can compromise the structural integrity of the trailer and lead to handling issues or failure during towing.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect the trailer spindles for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check for any cracks, corrosion, or loose components. Additionally, inspect the bearings, seals, and lubrication system to ensure they are in good condition. Perform routine maintenance tasks such as greasing the bearings and replacing worn-out parts as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Proper Weight Distribution: Ensure that the trailer’s load is properly distributed to avoid overloading the spindles or placing excessive stress on specific components. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the trailer’s maximum load capacity and distribute the weight evenly across the axles. Improper weight distribution can lead to instability, reduced braking performance, and increased risk of accidents.
- Appropriate Speed and Driving Behavior: Adhere to safe driving practices when towing a trailer. Maintain a safe and appropriate speed, considering the load, road conditions, and legal limits. Avoid sudden maneuvers, excessive braking, and rapid acceleration, as they can exert additional stress on the spindles and other towing components.
- Tire Maintenance: Properly maintained tires are essential for safe towing. Ensure that the trailer tires are properly inflated, have adequate tread depth, and are in good overall condition. Uneven tire wear or worn-out tires can affect the stability and handling of the trailer, potentially leading to accidents or tire blowouts.
- Proper Hitching and Coupling: Ensure that the trailer is properly hitched and coupled to the towing vehicle. Use a hitch that matches the trailer’s weight capacity, and ensure that the coupling mechanism is engaged securely. Improper hitching or coupling can result in trailer detachment, loss of control, or accidents.
- Trailer Braking System: If the trailer is equipped with brakes, ensure that the braking system is properly maintained and functioning correctly. Regularly inspect and test the brakes to ensure they provide adequate stopping power and are synchronized with the towing vehicle’s braking system.
- Safe Loading and Securing of Cargo: Properly load and secure the cargo in the trailer to prevent shifting, imbalance, or load loss during towing. Use appropriate tie-downs, straps, or cargo nets to secure the load and ensure it does not exceed the trailer’s weight capacity.
- Weather and Road Conditions: Consider the impact of weather and road conditions on towing safety. Adjust driving behavior and speed accordingly, especially in adverse weather conditions such as rain, snow, or strong winds. Be cautious on uneven or slippery road surfaces to maintain control and stability.
- Emergency Preparedness: Equip the towing vehicle and trailer with essential safety equipment, including a spare tire, jack, lug wrench, reflective triangles, and a fire extinguisher. Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures and know how to handle potential towing-related emergencies.
Following these safety considerations when using trailer spindles in towing can help ensure a safe and secure towing experience. It is essential to prioritize regular maintenance, adhere to recommended guidelines, and exercise caution while operating a trailer to prevent accidents, minimize risks, and protect both yourself and other road users.
What advantages do certain types of trailer spindles offer compared to others?
Trailer spindles come in various types, and each type offers unique advantages compared to others. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Straight Spindles:
Straight spindles are the most common type and offer several advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Straight spindles are relatively simple in design and construction, making them cost-effective compared to other types.
- Wide Availability: Straight spindles are widely available, making them easy to find and replace if needed.
- Easy Maintenance: Straight spindles are relatively easy to maintain and service, requiring fewer specialized tools or techniques.
- Tapered Spindles:
Tapered spindles provide their own set of advantages:
- Increased Load Capacity: Tapered spindles are designed to handle higher load capacities compared to straight spindles of similar size. The tapered shape enhances their strength and load-bearing capabilities.
- Better Alignment: Tapered spindles offer improved wheel alignment as they allow for precise fitment of the wheel hub assembly. This helps in maintaining proper tracking and reduces tire wear.
- Enhanced Stability: The taper design of these spindles contributes to enhanced stability during towing, reducing the risk of wheel wobbling or vibrations.
- Drop Spindles:
Drop spindles offer specific advantages for certain trailer applications:
- Lowered Trailer Height: Drop spindles are designed to lower the trailer’s ride height, allowing for easier loading and unloading of cargo or equipment.
- Improved Ground Clearance: By lowering the trailer height, drop spindles can also improve ground clearance, reducing the risk of bottoming out on uneven terrain.
- Enhanced Aerodynamics: The lower trailer height achieved with drop spindles can improve aerodynamics, leading to potential fuel efficiency gains.
- Brake Spindles:
Brake spindles offer advantages when used with trailer braking systems:
- Integrated Braking: Brake spindles are designed to accommodate brake assemblies and provide a mounting point for the brake components, allowing for integrated braking systems.
- Improved Stopping Power: Brake spindles, when used with appropriate brake systems, enhance the trailer’s stopping power, improving overall safety during towing.
- Controlled Braking: Brake spindles provide better control and modulation of braking forces, allowing for smoother and more controlled stops.
It’s important to note that the advantages of certain types of trailer spindles may be more relevant to specific trailer applications or towing requirements. Consideration should also be given to factors such as load capacity, compatibility with other trailer components, and manufacturer recommendations when selecting the appropriate spindle type for a given application.
In summary, certain types of trailer spindles offer advantages over others. Straight spindles are cost-effective, widely available, and easy to maintain. Tapered spindles provide increased load capacity, better alignment, and enhanced stability. Drop spindles lower the trailer height, improve ground clearance, and enhance aerodynamics. Brake spindles offer integrated braking, improved stopping power, and controlled braking. Understanding the advantages of different spindle types helps in selecting the most suitable option based on specific trailer requirements and towing needs.

Can you describe the factors to consider when selecting trailer spindles for specific applications?
When selecting trailer spindles for specific applications, several factors should be taken into consideration. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors to consider:
- Trailer Type and Purpose:
The type of trailer and its intended purpose play a significant role in determining the appropriate spindles. Different trailers, such as utility trailers, boat trailers, RV trailers, or horse trailers, have varying weight capacities, load requirements, and operating conditions. Understanding the specific trailer type and purpose helps in selecting spindles that can handle the expected loads and provide optimal stability.
- Load Capacity:
The load capacity of the trailer is a crucial consideration when selecting spindles. It is important to determine the maximum weight the trailer will carry, including the weight of the cargo or equipment. Spindles must be chosen to accommodate the expected load capacity to ensure safe and reliable operation.
- Wheel Size and Configuration:
The size and configuration of the trailer wheels are important factors in spindle selection. The spindle should be compatible with the wheel hub assembly and match the wheel bolt pattern. Additionally, the spindle may need to accommodate specific wheel sizes or tire configurations, especially in trailers where different wheel sizes are used.
- Environmental Factors:
The operating environment of the trailer should be considered when selecting spindles. For trailers exposed to corrosive environments, such as boat trailers used in saltwater, spindles with corrosion-resistant coatings or materials should be chosen to ensure durability and longevity.
- Compatibility with Axle and Suspension:
The spindle should be compatible with the trailer’s axle and suspension system. Consideration should be given to the type of axle (leaf spring, torsion, etc.) and the suspension configuration to ensure proper fit and functionality. The spindle should work in conjunction with the axle and suspension system to provide optimal stability and performance.
- Manufacturer Recommendations:
It is important to consult the trailer manufacturer’s recommendations or specifications when selecting spindles. The manufacturer’s guidelines provide valuable information about the appropriate spindle type, size, and other factors specific to the trailer model. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations helps ensure compatibility and adherence to safety standards.
- Regulatory Requirements:
Depending on the region and specific trailer application, there may be regulatory requirements or standards that dictate the selection of spindles. It is essential to be aware of and comply with these regulations to ensure legal operation and safety compliance.
- Expert Advice:
When in doubt or faced with unique trailer requirements, seeking expert advice from trailer manufacturers, suppliers, or industry professionals is recommended. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their expertise and experience.
In summary, when selecting trailer spindles for specific applications, it is important to consider factors such as the trailer type and purpose, load capacity, wheel size and configuration, environmental factors, compatibility with axle and suspension, manufacturer recommendations, regulatory requirements, and seek expert advice when needed. Taking these factors into account ensures the appropriate selection of spindles that can handle the load, provide stability, and meet the specific requirements of the trailer and its intended use.


editor by Dream 2024-04-23